Exploring the landscape of autoimmune digestive diseases in 2025, this guide aims to shed light on the complexities of these conditions and how they impact individuals.
From the causes and risk factors to diagnosis, treatment, and lifestyle modifications, this comprehensive overview delves into the key aspects of understanding autoimmune digestive diseases in the upcoming year.
Overview of Autoimmune Digestive Diseases
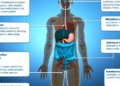
Autoimmune digestive diseases are conditions in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the digestive system, causing inflammation and damage to the gastrointestinal tract. This can lead to a wide range of symptoms and complications affecting the way the body processes food, absorbs nutrients, and eliminates waste.
Impact of Autoimmune Digestive Diseases
Autoimmune digestive diseases can have a profound impact on the digestive system, disrupting normal functioning and causing a variety of symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, constipation, and weight loss. In severe cases, these diseases can lead to malnutrition, intestinal damage, and other serious complications.
- Celiac Disease: A common autoimmune digestive disease where the immune system reacts to gluten, damaging the lining of the small intestine and affecting nutrient absorption.
- Crohn's Disease: Another prevalent autoimmune digestive disease characterized by chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, leading to abdominal pain, diarrhea, fatigue, and weight loss.
- Ulcerative Colitis: A condition that causes inflammation and ulcers in the colon and rectum, resulting in symptoms like bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, and urgency to have a bowel movement.
Prevalence of Autoimmune Digestive Diseases in 2025
In 2025, the prevalence of autoimmune digestive diseases continues to rise, with an increasing number of individuals being diagnosed with conditions like celiac disease, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis. Improved awareness, diagnostic tools, and research have contributed to better identification and management of these diseases.
However, the exact comparison to previous years may vary depending on the region and population demographics.
Causes and Risk Factors
Autoimmune digestive diseases can be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. These diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues, including those in the digestive system.
Genetics and Autoimmune Digestive Diseases
Genetics play a significant role in predisposing individuals to autoimmune digestive diseases. Certain genetic variations can increase the likelihood of developing these conditions. For example, individuals with a family history of autoimmune diseases are at a higher risk of developing autoimmune digestive diseases.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors can also trigger autoimmune digestive diseases in susceptible individuals. Factors such as diet, infections, and exposure to toxins can contribute to the development of these conditions. For instance, a diet high in processed foods and low in fiber may increase the risk of developing autoimmune digestive diseases.
Risk Factors by Disease Type
Different types of autoimmune digestive diseases have varying risk factors. For example, celiac disease is strongly associated with the consumption of gluten-containing foods, while inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis may have different triggers. Understanding these specific risk factors is crucial for effective management and prevention strategies.
Diagnosis and Screening
Autoimmune digestive diseases are diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests, imaging studies, endoscopy, and biopsy. These diseases can be challenging to diagnose due to their overlapping symptoms with other gastrointestinal conditions.
Significance of Early Detection
Early detection of autoimmune digestive diseases is crucial for effective management and treatment. Prompt diagnosis can help prevent complications, reduce disease progression, and improve the quality of life for patients.
- Early detection allows for timely initiation of appropriate treatment to control inflammation and autoimmune response.
- It can help prevent irreversible damage to the digestive system and improve long-term outcomes.
- Early diagnosis also enables healthcare providers to monitor disease activity and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Screening Procedures
Screening for autoimmune digestive diseases involves a series of tests and procedures to identify specific antibodies, inflammation, and damage in the digestive tract. Common screening methods include blood tests for autoimmune markers, imaging studies like CT scans or MRIs, endoscopic procedures such as colonoscopy or upper endoscopy, and tissue biopsy for confirmation.
Comparison of Diagnostic Methods
In 2025, advanced technologies have revolutionized the diagnosis of autoimmune digestive diseases. Traditional diagnostic methods like blood tests and endoscopy are still valuable, but newer techniques such as genetic testing, advanced imaging modalities, and biomarker analysis offer increased accuracy and precision in identifying these conditions.
- Advanced imaging technologies like confocal laser endomicroscopy provide real-time visualization of cellular changes in the digestive tract.
- Genetic testing can identify specific gene mutations associated with autoimmune diseases, aiding in personalized treatment approaches.
- Biomarker analysis helps in monitoring disease activity and predicting treatment response, leading to more targeted therapies.
Treatment and Management
Autoimmune digestive diseases are complex conditions that require a multifaceted approach to treatment and management. Currently, the treatment options available focus on alleviating symptoms, reducing inflammation, and managing immune system responses. However, effectively managing these diseases poses several challenges due to their chronic nature and varying severity among individuals.
Current Treatment Options
Current treatment options for autoimmune digestive diseases typically involve a combination of medications to control inflammation and suppress the immune system. Commonly used medications include corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biologics. Additionally, dietary modifications, such as avoiding trigger foods, may also play a crucial role in managing symptoms.
Challenges in Managing Autoimmune Digestive Diseases
One of the primary challenges in managing autoimmune digestive diseases is the variability of symptoms and disease progression among patients. Finding the right combination of medications that effectively control symptoms while minimizing side effects can be a complex process. Moreover, ensuring long-term adherence to treatment plans and lifestyle modifications can also be challenging.
Emerging Therapies and Treatments in 2025
In 2025, emerging therapies and treatments for autoimmune digestive diseases are focusing on targeted approaches that aim to modulate the immune response more selectively. Personalized medicine, including genetic testing to identify specific disease triggers, is also becoming more prevalent. Additionally, research into the gut microbiome and its role in autoimmune diseases is paving the way for innovative treatment strategies.
Holistic Approach to Managing Autoimmune Digestive Diseases
Adopting a holistic approach to managing autoimmune digestive diseases involves addressing not only the physical symptoms but also the psychological and emotional impact of the condition. Incorporating stress management techniques, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking support from healthcare professionals and support groups can complement traditional medical treatments and improve overall quality of life for patients.
Lifestyle Modifications and Support
Living with autoimmune digestive diseases can be challenging, but making certain lifestyle changes can help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Dietary Modifications
- Follow a well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support overall gut health.
- Avoid trigger foods that may exacerbate symptoms, such as gluten, dairy, or spicy foods, based on individual sensitivities.
- Consider working with a registered dietitian to create a personalized nutrition plan tailored to your specific needs.
Support Systems and Resources
- Join a support group or online community for individuals with autoimmune digestive diseases to connect with others facing similar challenges.
- Seek guidance from healthcare professionals, including gastroenterologists, nutritionists, and mental health therapists, to receive comprehensive care and support.
- Explore resources offered by patient advocacy organizations and non-profit groups dedicated to raising awareness and providing education about these conditions.
Mental Health Support
- Recognize the impact of autoimmune digestive diseases on mental well-being and seek counseling or therapy to cope with stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Practice relaxation techniques, mindfulness, or meditation to reduce symptoms triggered by emotional distress and improve overall mental health.
- Engage in activities that promote self-care and self-compassion, such as yoga, journaling, or spending time in nature, to enhance emotional resilience.
Summary
Wrapping up our discussion on Understanding Autoimmune Digestive Diseases in 2025, it is evident that advancements in treatment and management are crucial in enhancing the quality of life for those affected by these conditions.
General Inquiries
What are some common autoimmune digestive diseases?
Common autoimmune digestive diseases include Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and celiac disease.
How are autoimmune digestive diseases diagnosed?
Autoimmune digestive diseases are typically diagnosed through a combination of blood tests, imaging studies, and endoscopic procedures.
What lifestyle modifications can help manage autoimmune digestive diseases?
Lifestyle changes such as following a specific diet, reducing stress, and getting regular exercise can help manage symptoms of autoimmune digestive diseases.
What role does mental health support play in coping with autoimmune digestive diseases?
Mental health support is crucial in helping individuals cope with the emotional impact of living with autoimmune digestive diseases and can improve overall well-being.




![10 Best Whole Life Insurance for Seniors [Top-Rated Companies]](https://medic.radarbanten.co.id/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/BestTermLifeInsuranceCompanies-final-b2106835adde47b1ac9cf2942968ad13-120x86.png)